Motivation
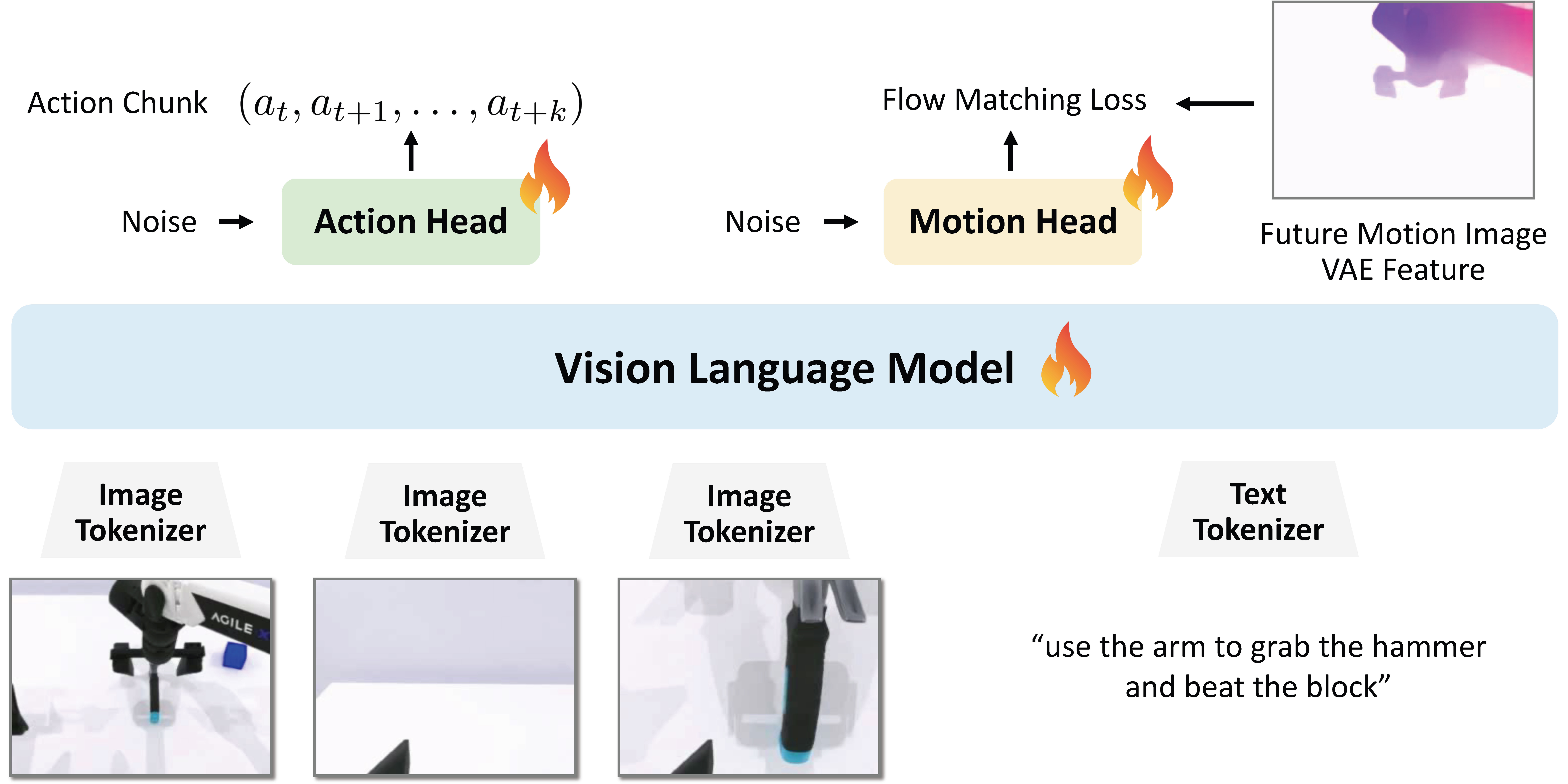
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have achieved remarkable progress in robotic manipulation by mapping multimodal observations and instructions directly to actions. However, they typically mimic expert trajectories without predictive motion reasoning, which limits their ability to reason about what actions to take.
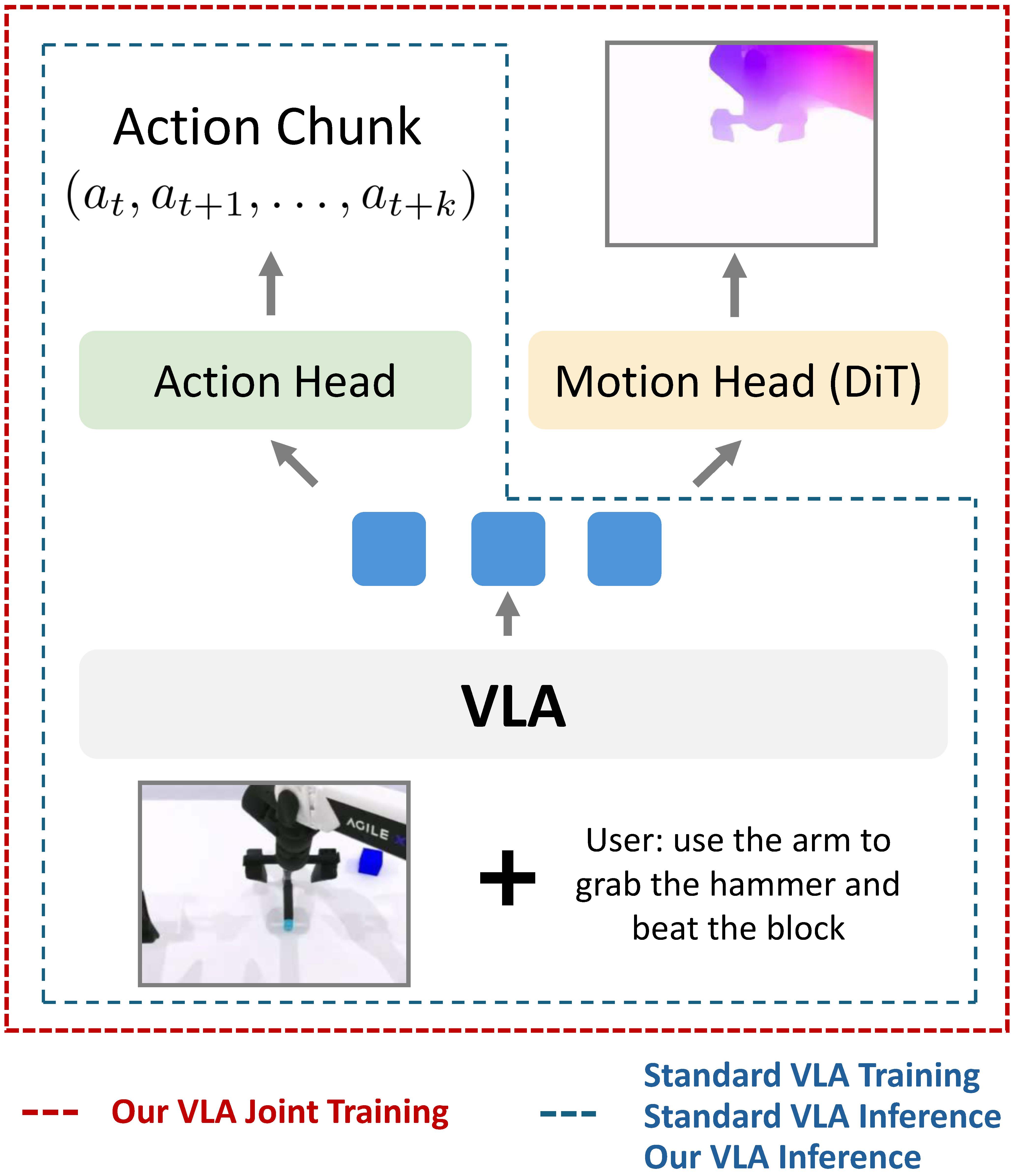
To address this limitation, we propose joint learning with motion image diffusion, a novel strategy that enhances VLA models with motion reasoning capabilities. Our method extends the VLA architecture with a dual-head design: while the action head predicts action chunks as in vanilla VLAs, an additional motion head, implemented as a Diffusion Transformer (DiT), predicts optical-flow-based future motion images that capture future dynamics. The two heads are trained jointly, enabling the shared VLM backbone to learn representations that couple robot control with motion knowledge. This joint learning builds temporally coherent and physically grounded representations without modifying the inference pathway of standard VLAs, thereby maintaining test-time latency.
Experiments in both simulation and real-world environments demonstrate that joint learning with motion image diffusion improves the success rate of pi-series VLAs to 97.5% on the LIBERO benchmark and 58.0% on the RoboTwin benchmark, yielding a 23% improvement in real-world performance and validating its effectiveness in enhancing the motion reasoning capability of large-scale VLAs.